7 Thai physics society news by Dheerawan Boonyawan
Following are the recent developments and activity plans of Thai Physics Society.
(1) 7th International School on Beam Dynamics and Accelerator Technology (ISBA24) will be held early between 1 and 9 November 2024. The venue is Chiang Mai University (CMU), Chiang Mai, Thailand.
-
The school is organized as an edition of the KEK-IINAS-NX series and hosted by PBP-CMU Electron Linac Laboratory (PCELL), Ching Mai University, the Hub of Talents for Particle Accelerators under the operation of the Thailand Center of Excellence in Physics, and the Synchrotron Light Research Institute (Public Organization).
- Due to the wide variety of accelerator usage, there is a strong demand for accelerator physicists and engineers from academic and industrial sectors. On the other hand, the opportunity to study the foundations of accelerators, including beam dynamics, accelerator design, and key technologies, is very limited. ISBA has been organized to provide such opportunities. The school can be a gateway to enter further advanced studies on the accelerator for graduate students and young researchers in the Asian region. Ref: https://conference-indico.kek.jp/event/275/
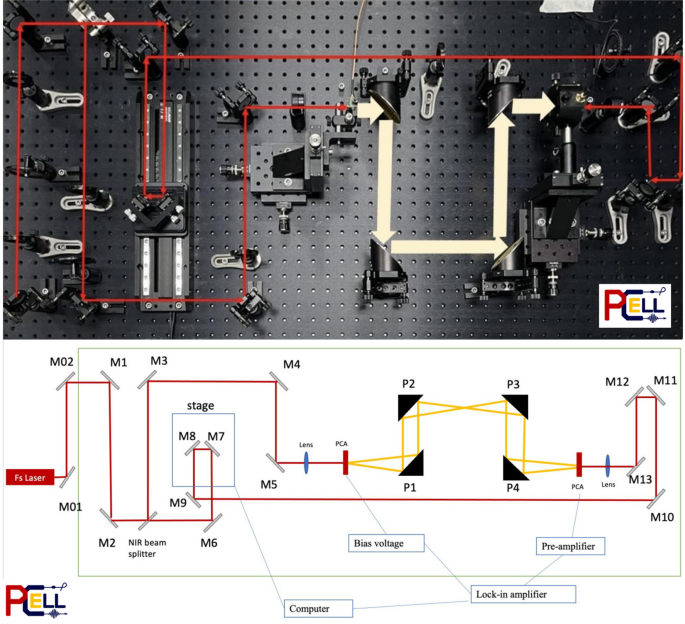
(2) PCELL THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) station to be installed and tested by the end of 2024.
-
The design and development of Thailand’s Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) system are expected to be installed and tested by the end of 2024. THz-TDS station uses short terahertz pulses to study and analyze the properties of matter in the time domain. It will obtain both amplitude and phase information of the electric field of terahertz radiation, enabling the analysis of material properties more comprehensively than experiments and analysis by FTIR spectroscopy.
-
Figure 11 presents the current installation and testing of the THz-TDS system. In fiscal year 2024, the newly developed THz-TDS system will be used in pilot experiments, including ionic liquids, perovskites, and low-dimensional materials. The experience and results from these experiments can be further applied to other users' applications of THz-TDS systems.
Here are some of the THz-TDS station of Thailand highlights.
-
Measure the transmittance and reflectivity properties of materials directly. This allows direct calculation of the electrical conductivity, dielectric constant, and complex refractive index, allowing a more complete and accessible understanding of the material's electrical conductivity.
-
A non-destructive testing technique that does not require additional processes such as DC conductivity measurement.
-
Examine the electrical conductivity of materials at the nanoscale since the frequency range of 0.4 to 2.5 THz corresponds to the size range of 10 to 20 nm.
Features of THz-TDS Station.
-
Spectral range: 0.4–2.5 THz
-
Scan range: 10 to 20 nm
-
THz spot size: millimeter level (used to indicate the size of the sample)
-
Repetition rate: 84 MHz
Ref.: https://www.infraredfel-thailand.org.
The THz-TDS station is based on particle accelerator. The particle accelerator, a powerful thrust in scientific studies, was used solely for nuclear and particle physics for the first several decades. Still, the usage was later spread out to broader fields. That includes other physics fields, material science, chemistry, biology, humanities, industrial and medical applications, etc. The THz-TDS station of Thailand is based on the PBP-CMU Electron Linac Laboratory in Thailand. Here is a list of Free-electron laser/THz laboratories around the world:
-
PBP-CMU Electron Linac Laboratory, PCELL, Thailand
-
Free-Electron Lasers for Infrared eXperiments, FELIX, Netherlands
-
Electron Linac for beams with high Brilliance and low Emittance, ELBE, Germany
-
Fritz-Haber-Institut Free-Electron Laser, FHI FEL, Germany
-
The Infrared Laser Center of Orsay, CLIO, France
-
Novosibirsk Free Electron Laser of terahertz range, NovoFEL, Russia
-
The University of California, Santa Barbara free-electron laser, UCSB FEL, USA
-
Jefferson Lab Free-Electron Laser, JLab FEL, USA
-
Kyoto University Free Electron Laser, KU-FEL, Japan
References
-
J.J. Hopfield, Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79(8), 2554–58 (1982)
-
J.J. Hopfield, Neuronswith graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81(10), 3088–92 (1984)
-
J.J. Hopfield, Artificial neural networks. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 4(5), 3–10 (1988)
-
G.E. Hinton, Computation by neural networks. Nat. Neurosci. 3(11), 1170 (2000)
-
J.J. Hopfield, Pattern recognition computation using action potential timing for stimulus representation. Nature 376(6535), 33–36 (1995)
-
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G.E. Hinton, Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–44 (2015)
-
A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
-
D.E. Rumelhart, G.E. Hinton, R.J. Williams, Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088), 533–36 (1986)
-
Editorial, 72% of SPM graduates prefer being influencers, E-Hailing drivers,” theSun, Aug 3, 2022. https://thesun.my/style-life/going-viral/72-of-spm-graduates-prefer-being-influencers-e-hailing-drivers-KX9536950. Accessed 24 Oct 2024.
-
R. Loheswar, Experts call for early-years STEM education to address critical engineering labour shortage in Malaysia. MalayMail, May 22, 2024. https://www.malaymail.com/news/malaysia/2024/05/22/experts-call-for-early-years-stem-education-to-address-critical-engineering-labour-shortage-in-malaysia/134795. Accessed 24 Oct 2024
-
R.P. Feynman, The Pleasure of Finding Things Out: The Best Short Works of Richard P. Feynman (Perseus Books, 1999)
-
Todd Siler, Breaking the Mind Barrier: The Artscience of Neurocosmology (Simon & Schuster, 1997)
-
R.S. Root-Bernstein, T. Siler, A. Brown, K. Snelson, ArtScience: integrative collaboration to create a sustainable future. LEONARDO 44(3), 192 (2011)
-
A. S. Eddington, Space, Time and Gravitation: An Outline of the General Relativity Theory (Cambridge University Press, 1920)
-
M. Kumar, Quantum: Einstein, Bohr, and the Great Debate About the Nature of Reality (W.W. Norton & Company, 2011)
-
Malaysia Education Blueprint 2013-2025, Prime Minister's Office of Malaysia. https://www.pmo.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Malaysia-Education-Blueprint-2013-2025.pdf
-
A. Osman, L. Halim, N.M. Arsad, Fundsof knowledge of the Semai Orang Asli children in science learning: a needs analysis. Int. J. Educ. 15(2), 48–65 (2023)
-
N. Z. Che Ghani, Implementation of Forest STEM Module based on Moral Values in Indigenous Education (Master’s thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
Authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.